- Metal 3D Printing Materials & Specifications
- Aluminum AlSi10Mg
- Cobalt Chrome MP1
- Maraging Steel MS1
- StainlessSteel GP1
- Stainless Steel PH1
- Titanium Ti64
- The Metal 3D Printing Process
- Metal 3D Printing Finishes
- What are the Advantages of Metal 3D Printing?
- Metal 3D Printing Applications
- Metal 3D Printing History
- Metal 3D Printing Quote
Metal 3D printing is also known as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLM). This additive layer technology is used to produce metal parts that may be to complex or cost prohibitive to manufacture by conventional means. A metal 3D printer utilizes a laser beam to melt 20- to 60-micron layers of metal powder on top of each other. Powdered metal is spread across the entire build platform and selectively melted to previous layers. This additive process allows metal parts to be grown out of a bed of powdered metal. 3D metal printing is similar to polymer-based Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printers that use powder bed fusion.
3D metal printed parts from Fathom are fully dense metal with excellent mechanical properties. There other metal 3D printing processes that use a binder with the metal powder, however, those processes produce parts that are not fully dense metal. DMLS and DMLM can produce parts with complex geometries that traditional CNC machining processes are incapable of manufacturing. Examples of metal 3D parts include molds and inserts, ductwork, and rapid tooling.
Metal 3D printing materials include stainless steel, cobalt chrome, maraging steel, aluminum, nickel alloy, and titanium.
Metal 3D Printing Materials & Specifications
Metal 3D printing is capable of producing durable parts from metal powders. These parts can be complex, intricate, and elaborate all while maintaining strength and durability.
| Material | Alloy Designation | Layers | Hardness | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (PH1) | 15-5 PH, DIN 1.4540 and UNS S15500 | 20 or 40 Micron Layers | 30-35 HRC Built, Post Hardened to 40 HRC | High Hardness and Strength | Prototype / Production Parts |
| Stainless Steel (GP1) | 17-4, European 1.4542, German X5CrNiCuNb16-4 | 20 or 40 Micron Layers | 230 ± 20 HV1 Built, Ground & Polished to 250-400 HV1 | High Toughness and Ductility | Engineering Applications |
| Cobalt Chrome (MP1) | ISO 5832-4 & ASTM F75 | 20, 40 or 50 Micron Layers | 35-45 HRC Built | High Temperature Resistance | Turbines and Engine Parts |
| Maraging Steel (MS1) | 18% Ni Maraging 300, European 1.2709, German X3NiCoMoTi 18-9-5 | 20 or 40 Micron Layers | 33-37 HRC Built, Post Hardened to 50-56 HRC | Easily to Machine and Excellent Polishability | Injection Molding Tooling, Conformal Cooling |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | Typical Casting Alloy | 30 Micron Layers | Approx 119 ± 5 HBW | Low Weight, Good Thermal Properties | Automotive, Racing |
| Nickel Alloy IN718 | UNS N07718, AMS 5662, AMS 5664, W.Nr 2.4668, DIN NiCr19Fe19NbMo3 | 40 Micron Layers | 30 HRC Built, Post Hardened 47 HRC | Heat and Corrosion Resistant | Turbines, Rockets, Aerospace |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | ASTM F138 | 20 Micron Layers | 85 HRB | Corrosion and Pitting Resistant | Surgical Tools, Food and Chemical Plants |
| Titanium Ti-64* | ASTM F2924 | 30 or 60 Micron Layers | 320 ± 15 HV5 | Light Weight, High Strength and Corrosion Resistant | Aerospace, Motorsport Racing |
| Titanium Ti-64 ELI* | ASTM F136 Properties | 30 or 60 Micron Layers | 320 ± 15 HV5 | Corrosion Resistance, Biocompatibility | Medical, Biomedical, Implants |
*Contact a Fathom expert for more information.
DMLS Parts in As Soon As 3 Days / / Get A Quote
Aluminum AlSi10Mg
AlSi10Mg is a typical casting alloy with good structural properties. This material is used for cast parts with thin walls and complex geometry. The alloying elements silicon and magnesium lead to high strength and hardness. The alloy also features good dynamic properties and can be used for parts subjected to high loads. Parts in Aluminum AlSi10Mg are ideal for applications that require a combination of good thermal properties and low weight.
Aluminum AISi10Mg Properties
- High Strength
- Hardness
- Good Dynamic Properties
Aluminum AlSi10Mg Applications
- Direct Manufacture of Functional Prototypes
- Low Volume Production Runs
- Products or Spare Parts
- Automotive
- Engineering
- Motor Racing
- Aerospace
- Prototype Parts for Aluminum Die Casting
Cobalt Chrome MP1
Cobalt Chrome MP1 produces parts in a cobalt-chrome-molybdenum-based super alloy. This class of super alloy is characterized by having excellent mechanical properties like strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance. Such alloys are commonly used in biomedical applications such as dental and medical implants as well as for high-temperature applications such as in aerospace engines.
Cobalt Chrome MP1 Properties
- Increased Strength, Temperature and Corrosion Resistance
- Improves Mechanical Properties with Increased Temperature Resistance up to 500-600 °C
- Conforms to the Chemistry Composition UNS R31538 of High Carbon CoCrMo Alloy
- Ensures Nickel-Free (< 0.1 % nickel content) Composition
- Fulfills Mechanical and Chemical Specifications of ISO 5832-4 & ASTM F75 for Cast CoCrMo Implant Alloys
Cobalt Chrome MP1 Applications
- High-Temperature Engineering Applications (e.g. turbines, medical implants)
Maraging Steel MS1
Maraging Steel MS1 is a martensite-hardenable steel. Its chemical composition corresponds to US classification 18% Ni Maraging 300, European 1.2709, and German X3NiCoMoTi 18-9-5. This kind of steel is characterized by having excellent strength combined with high toughness. The parts are easy to polish and machine with CNC finishing processes after the building process. Parts can be easily hardened in post processing to more than 50 HRC. Marging Steel applications include tooling and high performance parts.
Maraging Steel MS1 Properties
- Easy to Machine
- Age Hardening up to Approximately 54 HRC
- Good Thermal Conductivity
Maraging Steel MS1 Applications
- Series Injection Molding for High-Volume Production
- Tooling Applications (e.g., Aluminum Die Casting)
- High-Performance Parts
Stainless Steel GP1
Stainless Steel GP1 has a chemical composition that corresponds to US classification 17-4, European 1.4542, and German X5CrNiCuNb16-4. This kind of steel is characterized by having good mechanical properties; excellent ductility in laser processed state, and is widely used in a variety of engineering applications. This material is ideal for many part-building applications such as functional metal prototypes, small series products, individualized products, or spare parts.
Stainless Steel GP1 Properties
- Good Mechanical Properties
- Excellent Ductility
Stainless Steel GP1 Applications
- Engineering Applications Including Functional Prototypes
- Small Series Products
- Individualized Products or Spare Parts
- Parts Requiring High Toughness and Ductility
Stainless Steel PH1
Stainless Steel PH1 has a chemical composition that conforms to the compositions of 15-5 PH, DIN 1.4540, and UNS S15500. This kind of steel is characterized by having excellent mechanical properties, especially in the precipitation-hardened state. Stainless Steel PH1 is widely used in a variety of medical, aerospace, and other engineering applications requiring high hardness and strength. This material is ideal for many part-building applications such as functional metal prototypes, small series products, individualized products, or spare parts.
Stainless Steel PH1 Properties
- Very High Strength
- Easily Hardenable up to Approx. 45 HRC
Stainless Steel PH1 Applications
- Engineering Applications Including Functional Prototypes
- Small Series Products
- Individualized Products or Spare Parts
- Parts Requiring High Toughness and Hardness
Titanium Ti64
Titanium Ti64 is a Ti6Al4V alloy. This common, light alloy is characterized by having excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance combined with low specific weight and biocompatibility. The ELI version (extra-low interstitials) has a very high purity. Titanium is good for aerospace and engineering applications as well as biomedical implants.
Titanium Ti64 Properties
- Light Weight with High Specific Strength Per Density
- Corrosion Resistance
- Biocompatibility
- Laser-Sintered Parts Fulfill Requirements of ASTM F1472 (for Ti6Al4V) and ASTM F136 (for Ti6Al4V ELI) Regarding Maximum Impurities
- Very Good Bio-Adhesion
Titanium Ti64 Applications
- Aerospace and Engineering Applications
- Biomedical Implants
Selecting the best material for a metal 3D printing project is important. The experts at Fathom can help you select the most appropriate material for your project. Not sure what you need? Talk to a Fathom expert today!
The Metal 3D Printing Process
The basic metal 3D printing methods all involve producing a part by adding material one layer at a time. First, the build chamber is filled with argon or another inert gas. The gas is used to minimize the oxidization of the metal material. A thin layer of the powdered material is spread over the build platform. A powerful laser is used to fuse or sinter the powdered metal granules to create a cross section of the part. The build platform moves down one level and then another layer of metal powder is spread across the build platform. The laser then fuses the next layer to the previous layer. The process repeats itself until the part is complete. Support structures made of the same material are used to attach the part to the build platform. Support structures will also be used to hold up overhangs or complex geometries. Support structures will need to be removed in post processing. The part is detached from the build platform using cutting, wire-EDM, or machining. Interior support structures are cut out in the same manner. The completed part is excavated out of the powder bed and excess powder is removed before sending the part to be heat-treated.
Metal 3D printing methods include //
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM) //A laser melts layers of powdered metal material in successive layers.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM) //The same process as SLM, but an electron beam replaces the laser.
- Laser Deposition Welding (LMD) // A metal powder is layered on a base material and fused with no pores or cracks.
- Metal Powder Application (MPA) // Powder particles are accelerated in a carrier gas and then applied to a previously printed layer or substrate using a powder jet.
Once a part has been built using one of the above metal 3D printing processes, the part moves on to post-processing. Post-processing may include a number of techniques. These steps include removing any loose powder, removing support structures, and thermal annealing. The surface quality of the part may also be improved with media blasting, metal plating, micromachining, or polishing. Holes or threads may be created using CNC machining.
Distinguishing between each metal 3D printing process can be confusing as some of the processes are very similar. Some of the most common questions surrounding metal 3D printing terminology include //
What is the difference between DMLS and SLM? Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) both use a laser to scan and fuse or melt metal powder particles in order to bond them together and create a part in layers. Both processes use metal in granular form and both methods are a type of powder bed fusion 3D printing. The primary difference between the two is in the particle bonding process. While DMLS uses metal alloy material with variable melting points that bond at high heat, SLM uses metal powders with a single melting temperature. Both SLM and DMLS are suitable for industrial use and engineering projects.
What is the Difference Between DMLM and DMLS? Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLM) are additive manufacturing processes that use lasers to melt metal powdered material to fuse particles together. In the DMLS process, the metal is only partially melted. In the DMLM process, the material is fully melted into a liquid, which then solidifies when cooled. DMLS is a term that may be used to describe either process.
Metal 3D printing will yield a high-quality part that is comparable to a metal part made with traditional manufacturing methods. The ability to produce strong, complex, and durable parts is just a few of the advantages of metal 3D printing. A Fathom metal 3D printing expert can help you decide on the right process for your next project.
Metal 3D Printing Finishes
There are several finishes and finishing processes that can be utilized for metal 3d printing. Options include:
Abrasive Blast (Grit & Ceramic)
Abrasive blasting removes imperfections, rust, or other contaminants from the surface of a part. It is often used in preparation for a coating application. Abrasive blasting methods include micro-abrasive blasting, bristle blasting, bead blasting, and more.
Shot Peen
Shot peening is used to add strength and reduce the stress profile of a part. Multiple shots are directed at the surface of the part. The shot peen causes deformation on the part surface. The deformation creates a compressive stressed layer that will protect the part and add durability.
Optical Polish
Optical polishing is used to create a micro-finish or super-finish on a surface for further processing. Optical polish is best used on projects with geometries in low quantities that are not tolerance dependent.
Electrochemical Polishing
Electrochemical polishing produces a mirror-like finish on metal surfaces and is sometimes used to prepare a metal part for additional finishing. The part is placed into an electrolytic solution alongside a cathode of copper or lead. An electric current moves through the solution, transferring metal ions to the part. The transferred material will smooth the surface of the part.
Abrasive Flow Machining
Abrasive flow machining is used for de-burring and polishing parts. Abrasive flow machining uses chemically inactive media. The abrasive material will polish the part and remove unwanted material.
Electroplating
Electroplating adds a metal layer to the outside of a part, increasing its strength and durability. Electroplating dissolves metal in an electrolytic solution and transfers it onto the surface of the part.
Micro Machining Process (MMP)
The micro machining process is used to produce a mirror-like finish with great technical precision while preserving the geometries of the part. The part is first mapped using a profile-meter to create a roughness profile. The part is then moved to an MMP envelope where micro-milling cutters begin to polish the part.
What are the Advantages of Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printed objects have excellent physical properties. They can be made with a wide range of materials, including super-alloys that are difficult to process using traditional manufacturing methods. A metal 3D printed product will perform well, is lighter in weight, and requires fewer assembly components. Using the metal 3D printing method allows companies to produce parts with complex geometries that may be unachievable using traditional manufacturing methods.
DMLS Parts in As Soon As 3 Days / / Get A Quote
Metal 3D Printing Applications
Metal 3D printing is a popular manufacturing method because it can reduce the weight of the part while adding durability and strength. These features have proven advantageous for a variety of industries including aerospace, healthcare, research and development, automotive, and more. DMLS may be used for numerous applications, including //
- Functional Prototypes
- Direct Digital Manufacturing
- Molds and Inserts
- Ductwork
- Rapid Tooling
- Spare Parts
- Rigid Housing
- Heatsinks and Heat Exchangers
Metal 3D Printing History
Metal 3D printing technology started in the 1980s. The following timeline is a summary of the history of metal 3D printing //
- 1980 / / The first laser sintering machine was developed by Dr. Carl Deckard of the University of Texas. The machine was used for plastic but presented an opportunity for metal 3D printing.
- 1986 / / Stereolithography technology is invented by Charles Hull
- 1988 / / Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) was invented by Carl Deckard and paved the way for the introduction of DMLS.
- 1989 / / Selective Laser Sintering is invented by Carl Deckard
- 1991 / / Binder Jetting in invented by Dr. Ely Sachs of MIT.
- 1995 / / ExOne licensed binder jetting for use with metal materials.
- 1995 / / The Fraunhofer Institute of Germany patents the melting of metal by lasers. EOS, a German company, and several universities also aided in the development of 3D metal printing.
- 2012 / / Large corporations GE, HP and DM began investing in metal 3D printing.
Other Metal 3D Printing Resources & References
Read through these other metal 3D printing resources, references and articles //
- 3D Printed Titanium Bike Parts
- Conformal Cooling
- DMLS in Aluminum, Inconel or Titanium – Is it worth it?
- Direct Metal Laser Melting Services
- DMLM vs. DMLS – Is There Really Any Difference?
- Color 3D Printing
- Investment Casting
- GPI Prototype Builds 3D Printed Inconel 718 Rocket Engine For SEDS at UCSD
- How Does DMLS Work?
- 3D Printed Guitar Parts
- Metal Additive Manufacturing Services
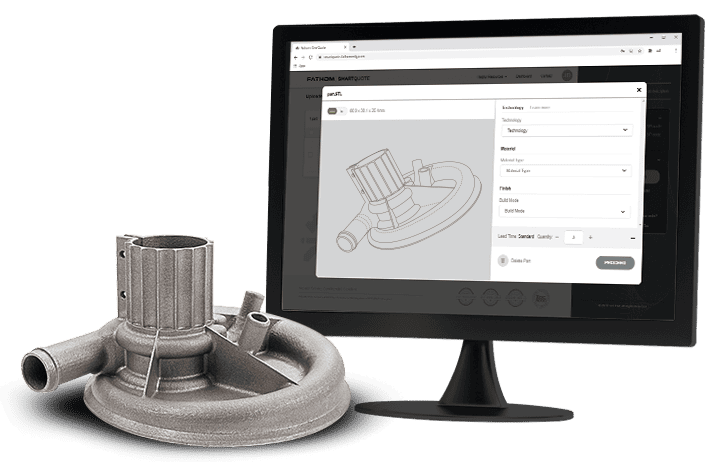
Metal 3D Printing Quote
Quickly get a quote on any metal 3D printing project today and have your parts in as soon as three days depending on project specifications.