Q.
I’ve heard that 3D printing technology is only suitable for making prototype parts. Is that true?
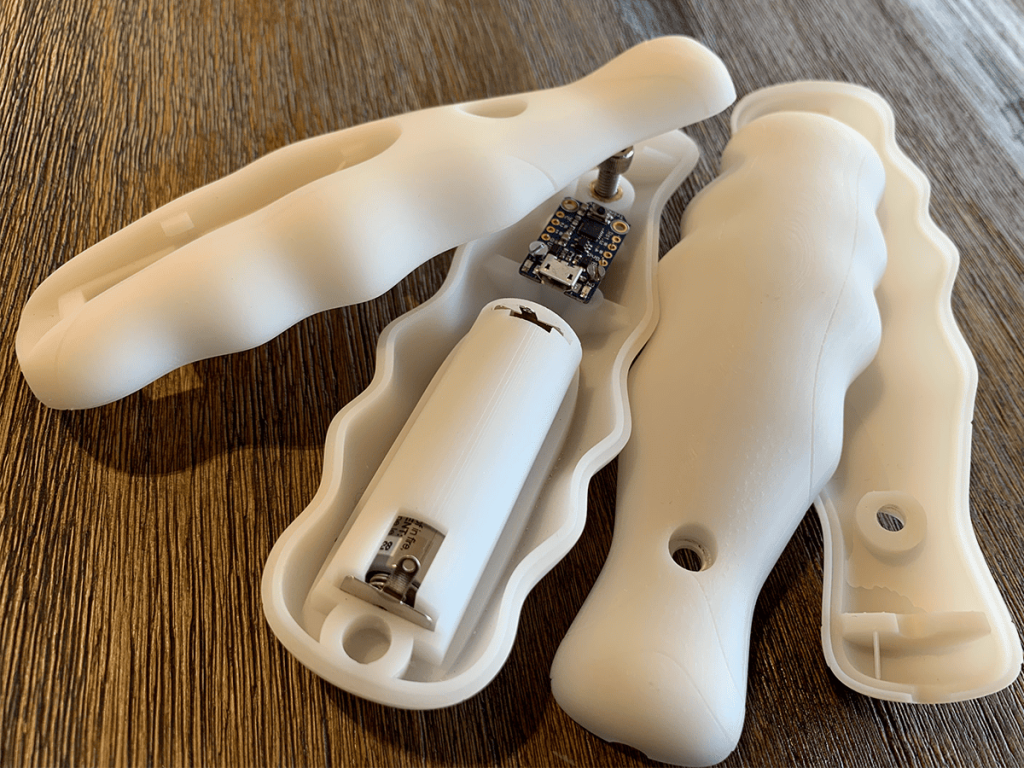
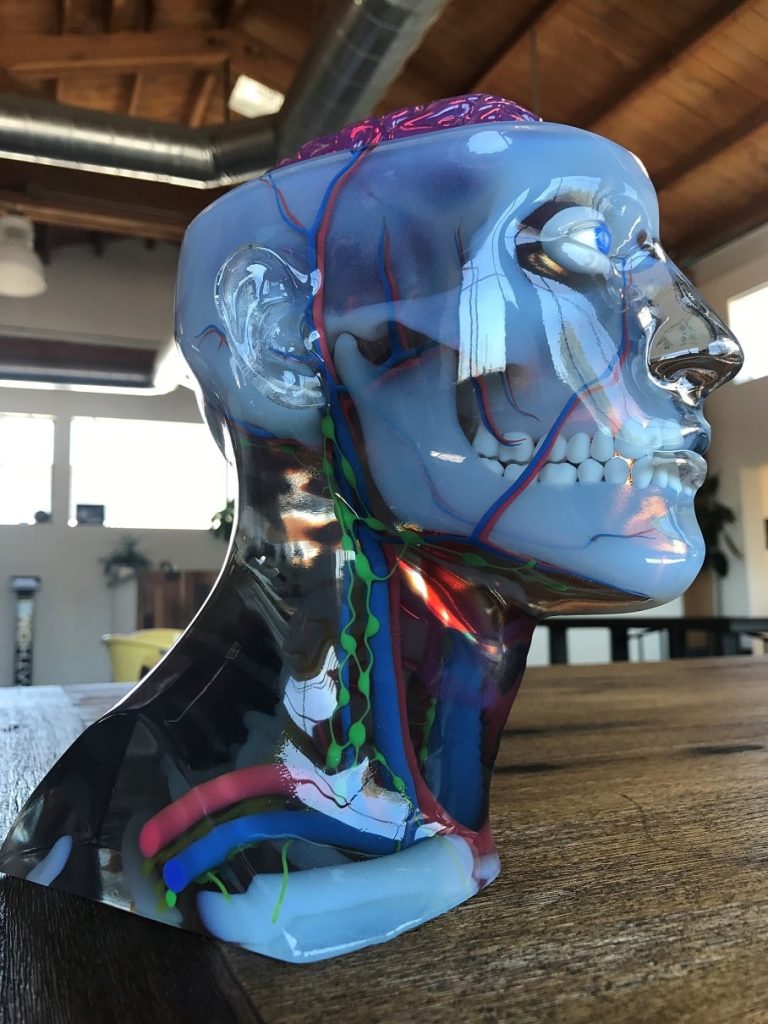
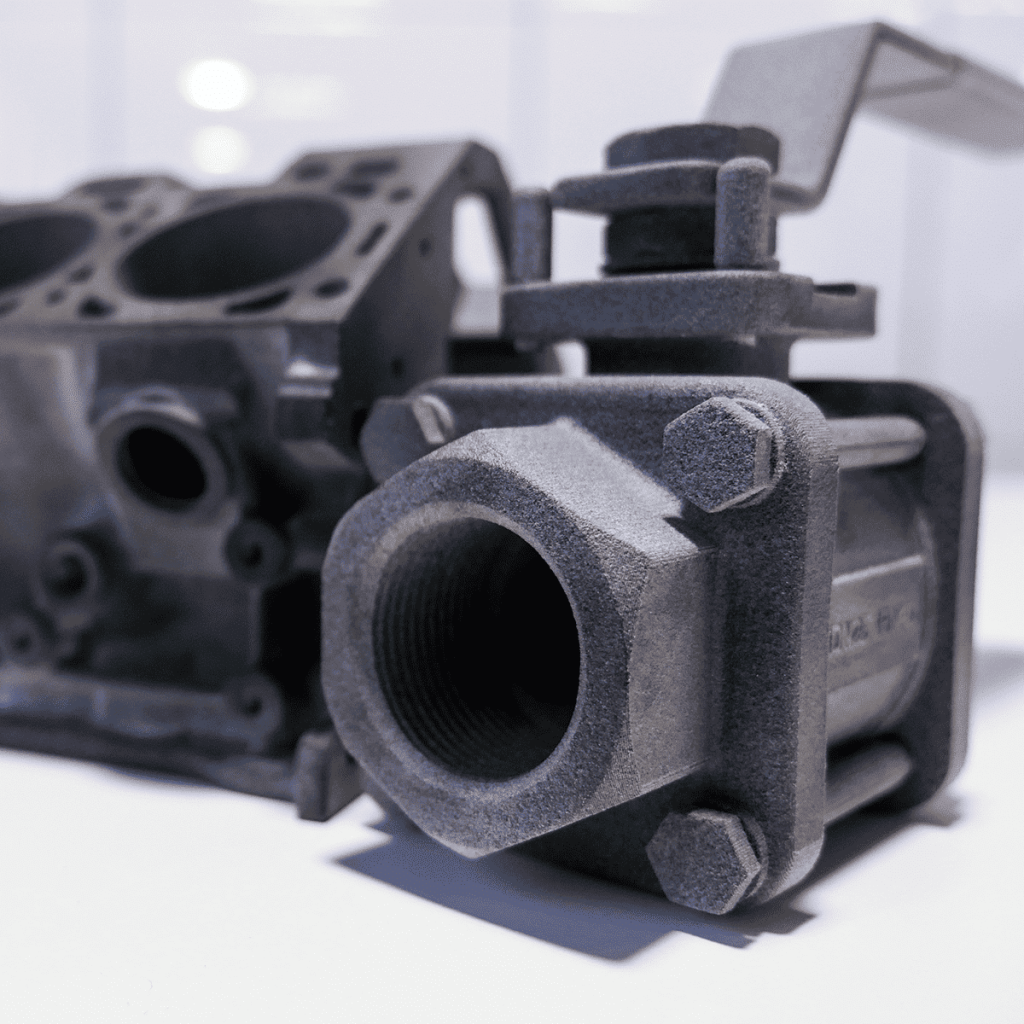
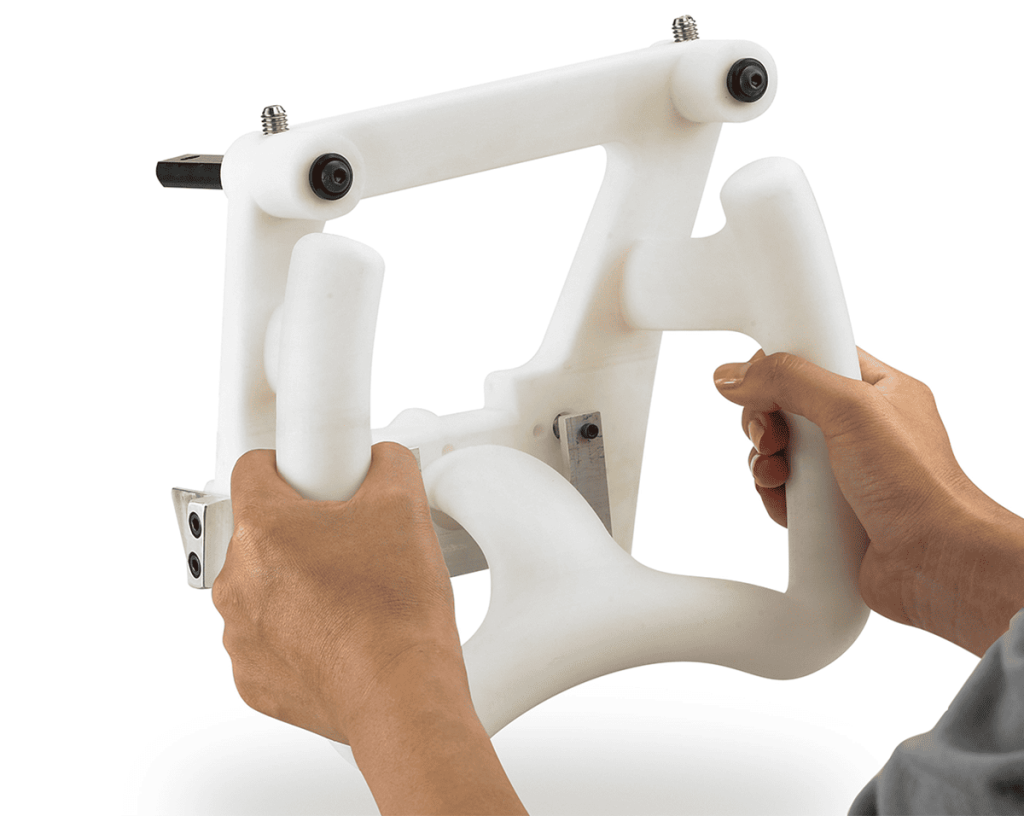
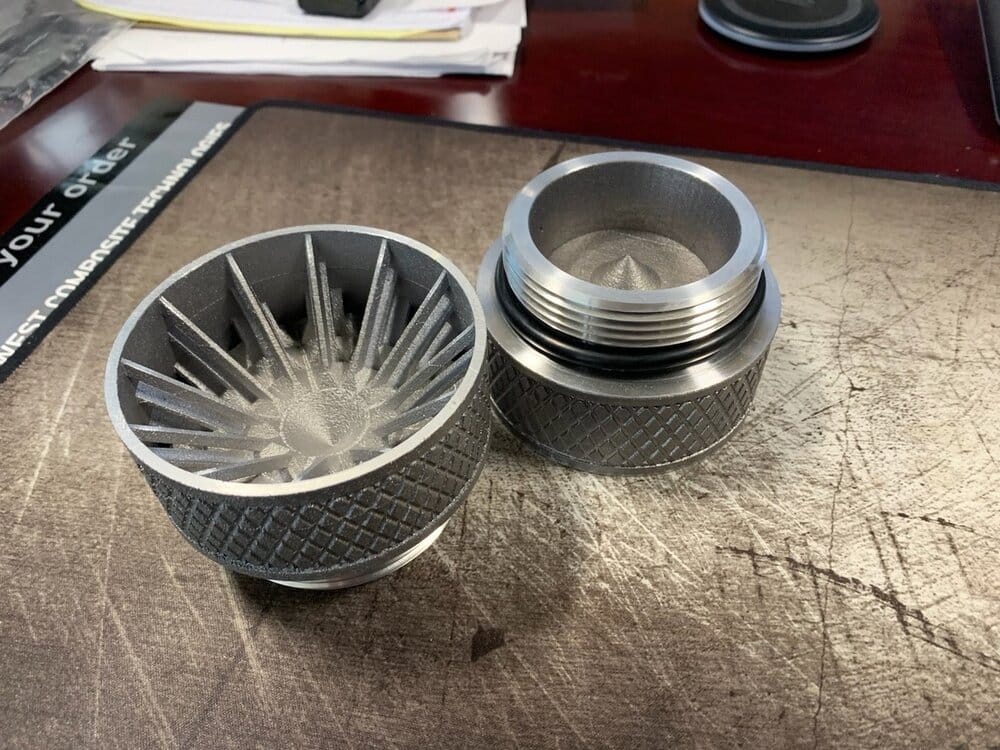
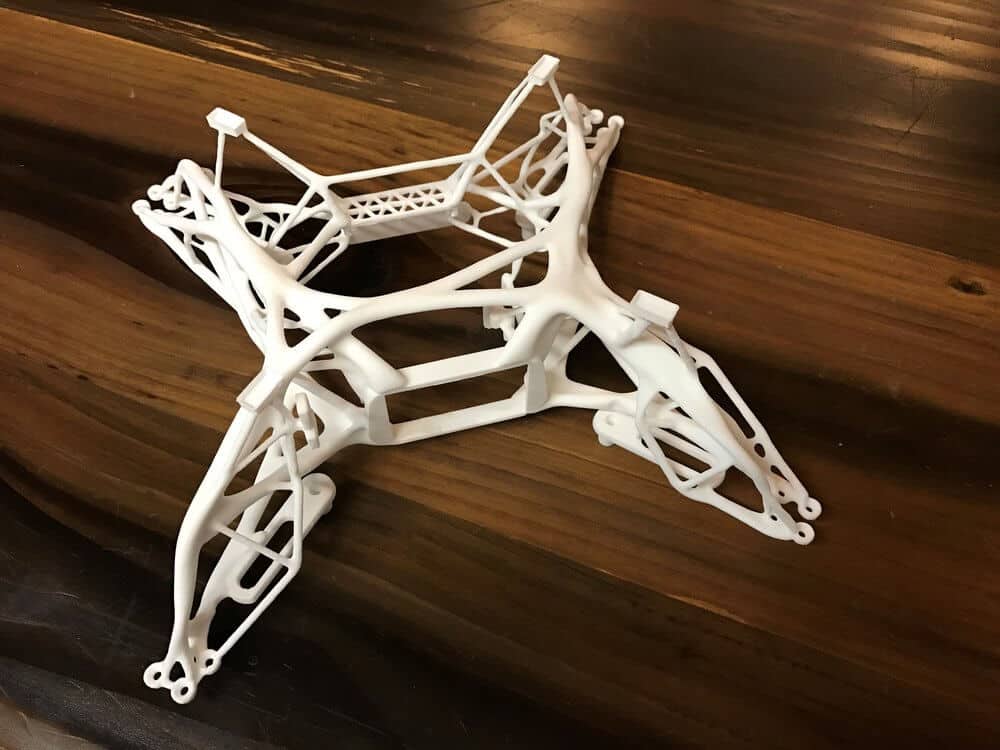
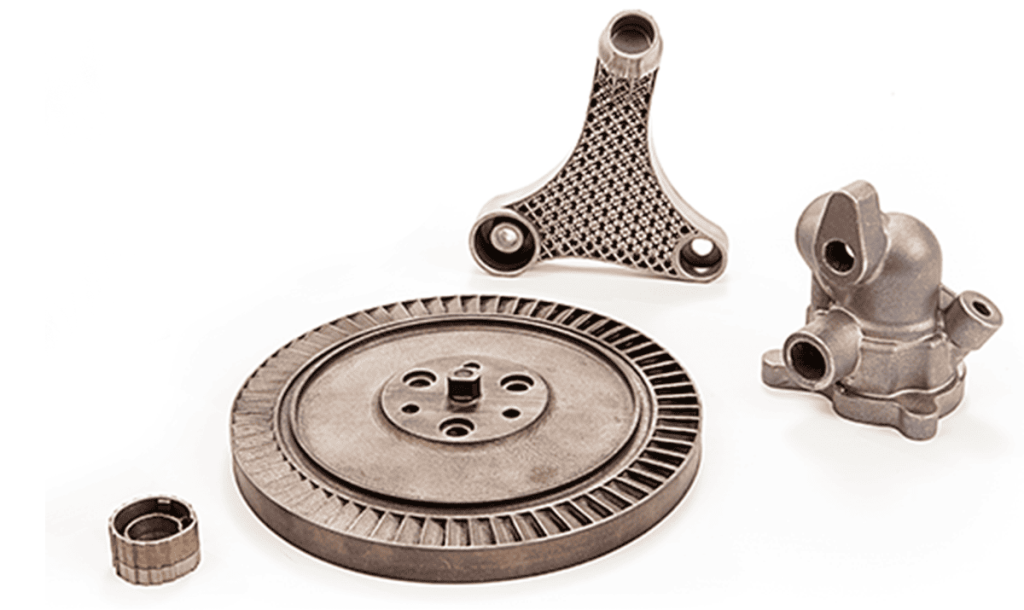
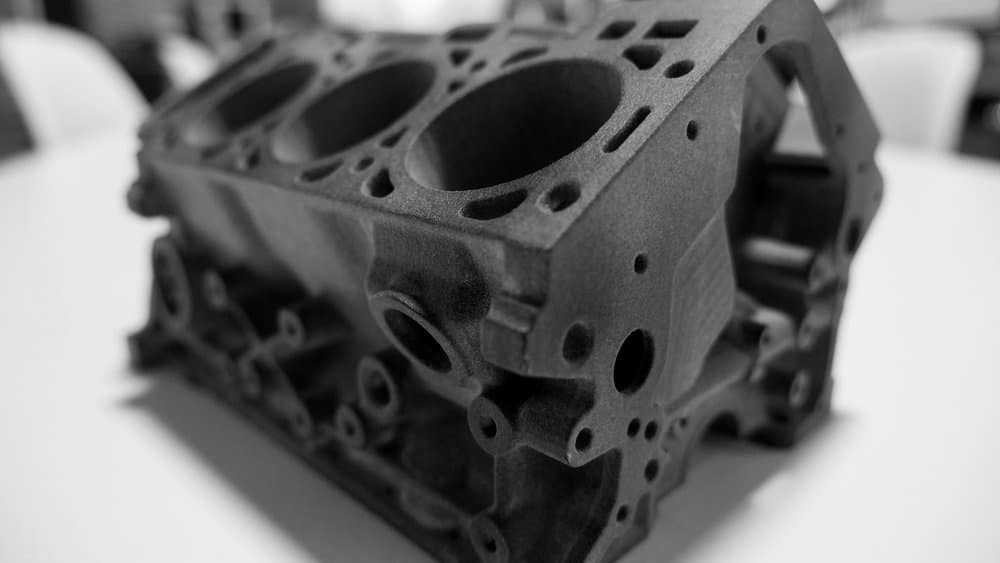
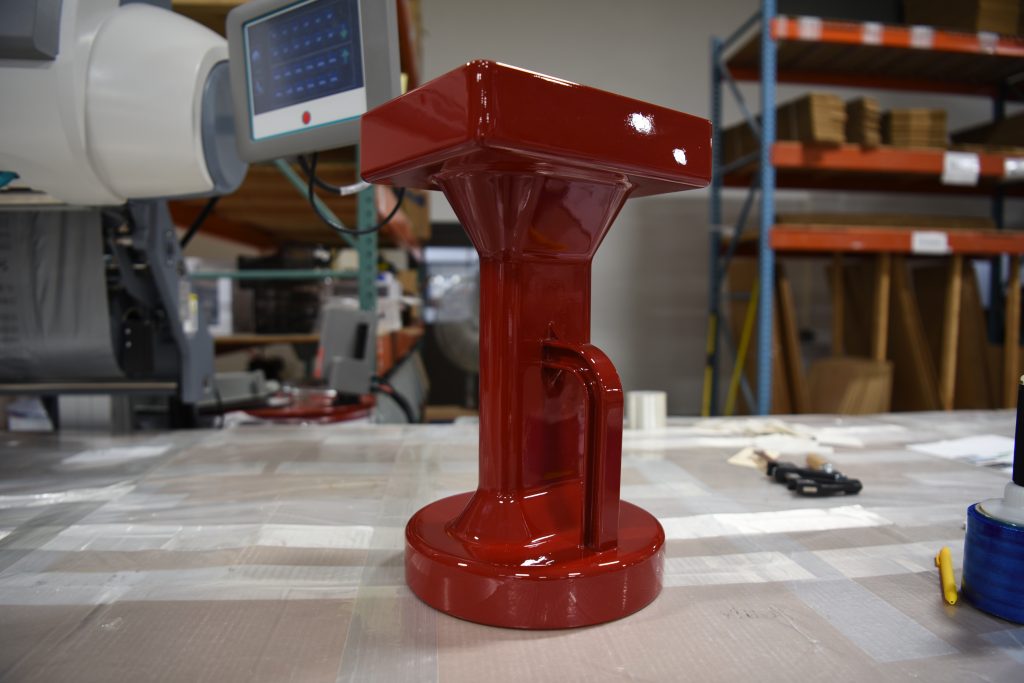
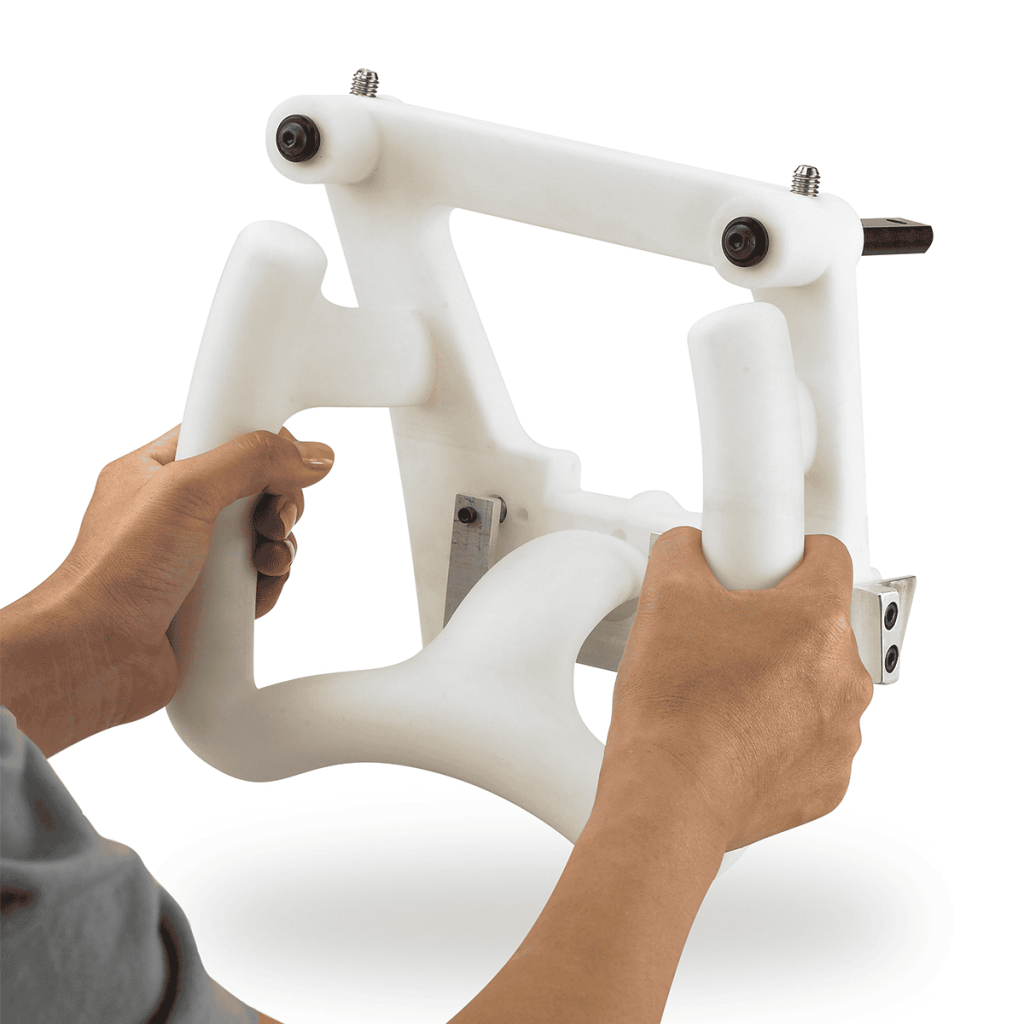
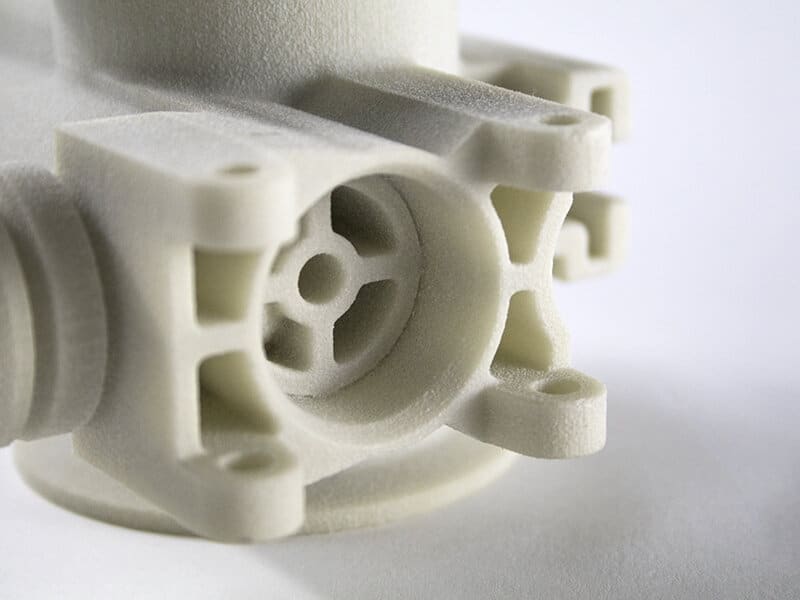
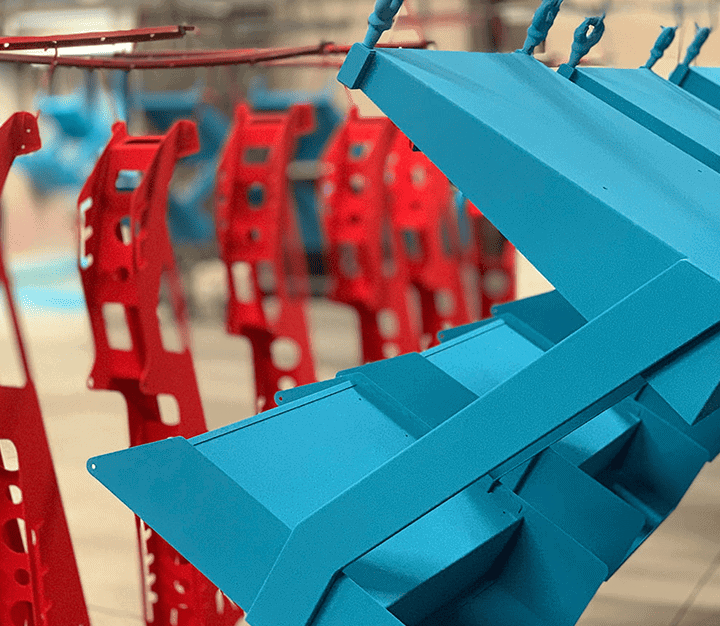
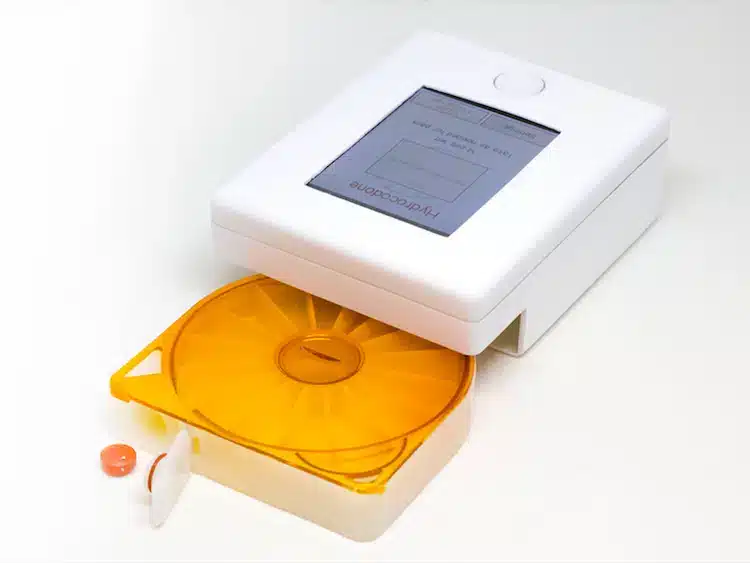
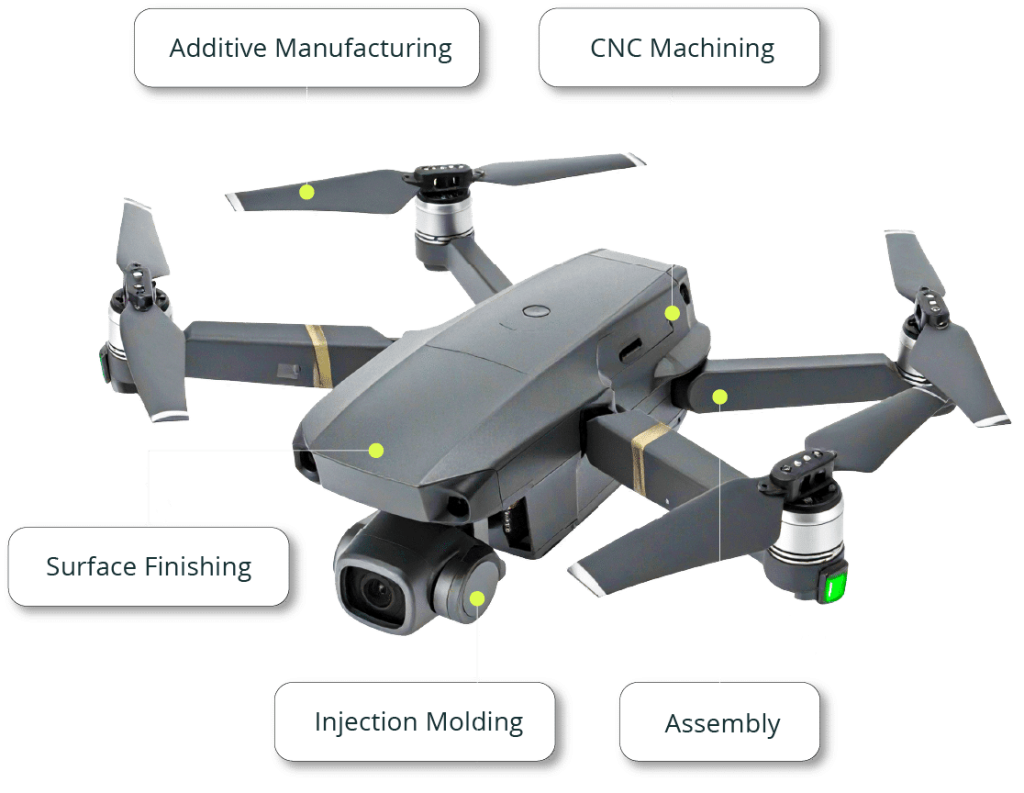
The versatility of commercial 3D printing has grown significantly during the last decade. It’s now used to make bridge- and full-production parts. Several industrial 3D printing processes can also be used to create durable jigs and workholding fixtures.