Q.
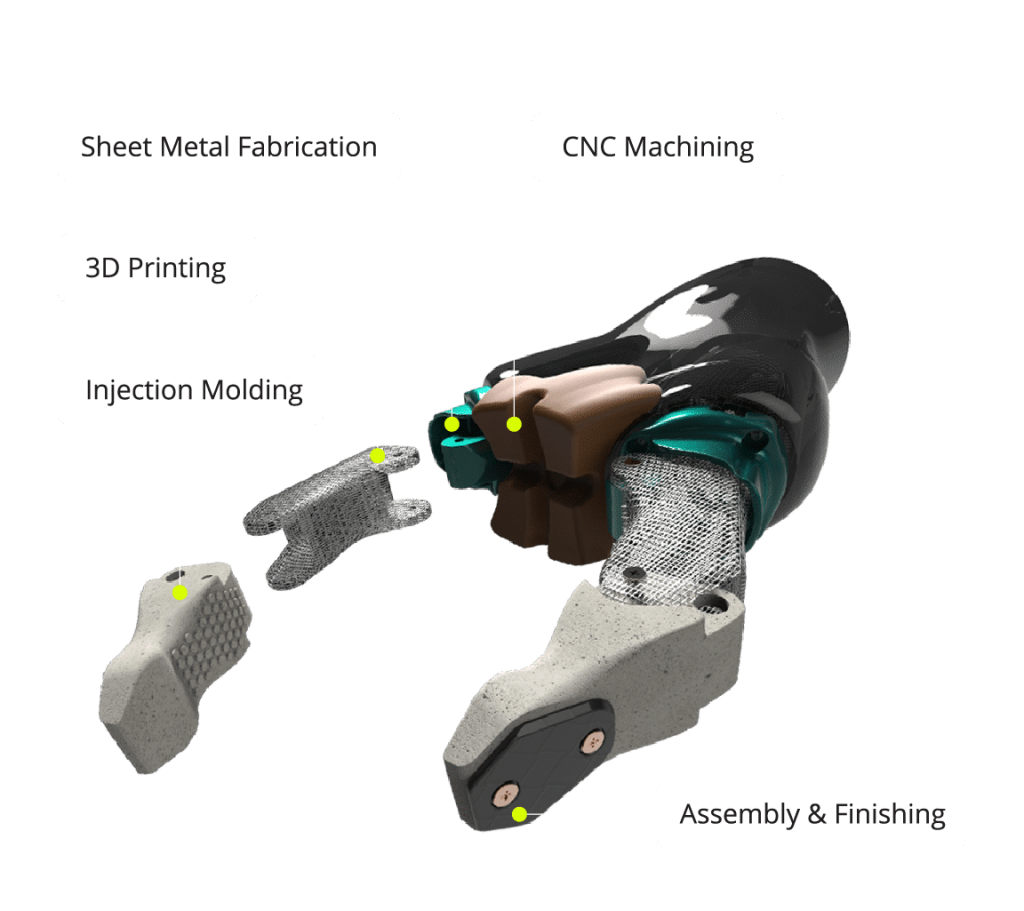
What types of materials can be CNC machined?
Metal and plastic are the most commonly machined materials. Foam and wood can also be shaped using CNC machining, ideal for creating molds for different types of casting and FRP part production.